The Definitive List of CNA Duties
Get Your Degree!
Find schools and get information on the program that’s right for you.
Powered by Campus Explorer
The Definitive List of CNA Duties
Patient Care
 One on one engagement with patients is a large part of what a CNA’s job is. This means assisting the elderly and disabled with whatever daily living tasks need to be done. This can range anywhere from dressing, bathing, toiletry, preparing and serving meals, passing out medications, hygiene, and answering patient requests. All CNA duties that revolve around patient care include:
One on one engagement with patients is a large part of what a CNA’s job is. This means assisting the elderly and disabled with whatever daily living tasks need to be done. This can range anywhere from dressing, bathing, toiletry, preparing and serving meals, passing out medications, hygiene, and answering patient requests. All CNA duties that revolve around patient care include:
- Prepare meals — Prepare meals for patients, taking into consideration any special diets a patient might have
- Serve meals — Serve meals (often lunch and dinner) to patients in the dining area, help patients who cannot feed themselves by directly assisting them
- Collect food trays — Collect food trays once patients have finished eating
- Get snacks/drinks — Get snacks and drinks for patients if requested
- Bathe patients — Most patients need bathing once a day, and if patients can’t wash themselves, CNAs must bathe and wash them in a quick process
- Dress patients — Dress patients as needed, either around lunchtime or before bedtime, or anytime where the patient needs new clothing
- Clean rooms — Basic housekeeping tasks such as dusting, sweeping, changing bedpans, and organizing rooms
- Toiletry — Help patients go to the toilet and assist them if necessary
- Move patients — Move patients in and out of their rooms to places they need to go
- Keep patients safe — Keep patients safe when performing CNA duties, taking into consideration any hazards and prevent patients from falling, getting hurt, etc.
- Make and change bedding — Make patients’ beds or change linens as necessary
- Collect laundry — Collect any dirty clothing or bed linens
- Collect samples — Collect patient blood, urine, or stool samples for lab tests
- Assist pre-surgery patients — Help prepare patients who are about to enter surgery
- Pass out medications — Carefully count and pass out medications for patients, taking into consideration any special instructions for specific patients
- Hygiene — Help patients clean teeth, shave, cut nails, brush hair, etc.
- Exercise — Help patients exercise when necessary
- Position patients — Help move patients into a comfortable position, prevent bed sores by moving patients to their sides
- Prepare medical equipment — Clean and prepare medical equipment for physicians or RNs to perform treatment
- Emotional support — Bond with patients, often by talking/listening to them or comforting them when they are in a bad mood or have fears or concerns
- Follow instructions of staff — Follow any instructions given to you by LPNs, RNs, or physicians and assist with any medical procedures as necessary
- Answer patient requests — Help assist patients with whatever they need when they press the call button (often to re-position them, get drinks/snacks, etc.)
Infection Control
Duties o f a CNA also includes infection control, which is a crucial aspect to consider. This entails preventing cross-contamination where germs can spread throughout the healthcare setting, which could be disastrous. CNA duties that revolve around infection control include:
f a CNA also includes infection control, which is a crucial aspect to consider. This entails preventing cross-contamination where germs can spread throughout the healthcare setting, which could be disastrous. CNA duties that revolve around infection control include:
- Wash hands often — Washing hands constantly prevents the spread of germs that you may have come into contact with to another patient or staff member
- Keep sick patients away from others — Keep sick patients from coming into contact with others, often by keeping them isolated or quarantined
- Clean soiled bed linens — Change soiled bed linens as necessary, replacing them with new sheets or replacing beds altogether
- Dispose materials with germs — Anything that may possess germs or bacteria must be safely disposed of, exercising universal precautions throughout the process
- Help patients stay clean — Ties into patient hygiene, with tasks such as bathing, grooming, trimming nails, shaving, etc.
- Handle patient samples with care — When taking blood, urine, or stool samples, it is necessary to exercise universal precautions while taking the samples as well as transporting them to the laboratory
- Keep up-to-date with current infection control techniques — Take continuing education courses to learn about all the latest techniques of infection control (could be optional and provide by your employer)
Monitoring Patient Health
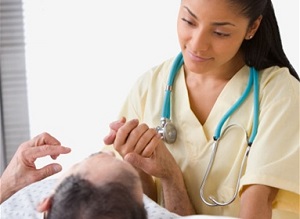 Certified nursing assistants are in charge of assisting the elderly and disabled, who are either ill or have gone through a traumatic experience and need help recuperating. As a result, CNA duties also include monitoring patient health for any unusual activity or changes in health. These duties of a CNA can include:
Certified nursing assistants are in charge of assisting the elderly and disabled, who are either ill or have gone through a traumatic experience and need help recuperating. As a result, CNA duties also include monitoring patient health for any unusual activity or changes in health. These duties of a CNA can include:
- Take patient vital signs — Take temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, etc. of patient, often done initially for a new patient and throughout their stay
- Monitor — Observe any changes in patient’s health, diet, behavior, complaints, mood, etc. and document changes (explained further below)
- Understand patient’s needs — Monitoring patient’s behavior and emotional state for any needs they might need, including re-positioning, addressing hunger/thirst, or if they need to go to the restroom
- Observing changes — Compare patient behavior, mood, etc. with previous nursing reports for any significant changes and find out why
- Dietary intake — Keep track of what the patient has eaten and drank
Record Keeping
 Record keeping is quite simple although it requires precise accuracy in documentation. Basically, you will be recording any changes to a patient’s health, behavior, or requests in a nursing report, which is crucial to the nursing staff in order to provide proper treatment as necessary. This tasks include:
Record keeping is quite simple although it requires precise accuracy in documentation. Basically, you will be recording any changes to a patient’s health, behavior, or requests in a nursing report, which is crucial to the nursing staff in order to provide proper treatment as necessary. This tasks include:
- Record dietary intake — Document what the patient has ate/drank and how much
- Record vital signs and changes — Document any changes to the patient’s vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate, temperature, etc.
- Report to staff — Report any changes or issues to other staff members (such as LPNs and RNs) and help to resolve these problems
- Record data — Record all data from equipment, computers, and observations
- Medication — Keep track of all medications administered
